With a wealth of structured data readily available, multi-disciplinary diagnostics can be significantly improved, as the aggregated information can foster collaborative efforts between different fields of expertise, such as radiology, pathology, and genomics. As a result, comprehensive clinical profiles can be built, leading to a more holistic and patient-centric approach to diagnostics and treatment planning.
In the dynamic landscape of healthcare, radiology plays a pivotal role in diagnosing and guiding treatment decisions. However, as the volume and complexity of imaging studies continue to rise, traditional reporting methods are increasingly challenged to meet the demands of modern radiology practice. This white paper explores the transformative potential of structured reporting—a technology poised to revolutionize radiology workflows and enhance patient care.
In recent years, radiology professionals have faced significant challenges. As highlighted in a study presented at RSNA 2023 by Tomas Bjerner, MD, PhD, of Linköping University, the data volume in CT and MRI studies requiring radiologists’ interpretation increased up to sixfold between 2009 and 2022. Yet, during the same timeframe, the number of exams merely doubled. Such larger, more complex cases intensify the cognitive load and overall work burden for radiologists, which can be underestimated when solely considering the total volume of imaging examinations1. Alarmingly, burnout rates among radiologists have reached as high as 54%2, emphasizing the critical need for achieving work-life balance, which, in turn, translates to enhanced patient care.
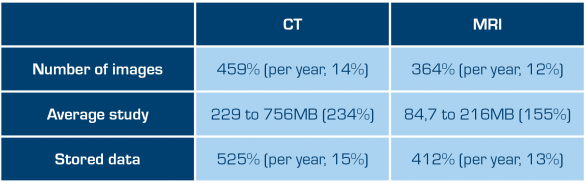
Increases in numbers of images and total data in CT and MRI exams for radiologists, 2009-2022
Technological advancements play a pivotal role in supporting radiologists and alleviating the burdens associated with their demanding work. Artificial intelligence (AI)-driven tools, automated image analysis, and other innovations have the potential to streamline the interpretation process, reduce manual workload, and enhance the efficiency of radiological workflow. These technologies enable radiologists to focus their expertise on critical decision-making aspects while automating routine tasks.
The evolution of radiology: from image interpretation to data-driven diagnostics
Traditionally, radiologists have been the gatekeepers of medical imaging, responsible for interpreting complex images to diagnose diseases and guide treatment plans. However, as radiology has become increasingly data-driven, their role has expanded to encompass data analysis, research, and patient care optimization3. This expanded role demands a more streamlined and efficient approach to data collection and report generation.
Adopting structured reporting in radiology facilitates in-workflow data collection and curation, creating the foundation for data-driven research and decision support. By standardizing the data format and utilizing structured fields, radiology reports can be transformed into valuable repositories of information that enable researchers and clinicians to mine insights, discover trends, and make evidence-based decisions.
In addition, structured reporting can contribute to the development of advanced decision-support tools, including AI and machine learning algorithms. By leveraging large datasets generated from structured reports, these technologies can identify patterns, generate predictions, and provide evidence-based recommendations, further enhancing the accuracy, efficiency, and relevance of radiology reporting and diagnostics.
The implementation of structured reporting ultimately paves the way for more data-driven, multi-disciplinary approaches to diagnostic medicine. By automating the collection and curation of clinical data, structured reporting becomes instrumental in advancing patient care, furthering medical research, and supporting the continuous growth of healthcare innovation.
Structured reporting’s role in reducing burnout and enhancing patient care
The steady increase in the number of studies radiologists must interpret, coupled with rising burnout rates, has been widely discussed for some time4,5. The field of radiology is undergoing a profound transformation, driven by the convergence of technological advancements and evolving patient care needs. At the heart of this transformation lies a fundamental shift in reporting practices that promises to revolutionize the way radiologists interact with medical images and contribute to patient care.
Incorporating structured reporting into radiology workflows not only enhances the overall consistency and clarity of reports but also significantly reduces the administrative burden faced by radiologists. One particularly advantageous aspect of structured reporting is its capacity to seamlessly integrate and “pull in” data from other healthcare systems, such as electronic medical records (EMR) and picture archiving and communication systems (PACSs), directly into the report. This streamlined process can significantly decrease the time spent on manual data entry and cross-referencing between various systems, leading to more efficient report generation and reduced workload.
Moreover, by avoiding manual data entry, the risk of errors stemming from issues like mistyping or incorrect manual calculations can be substantially minimized. Consequently, this improved efficiency allows radiologists to focus on more critical aspects of patient care, fostering a better work-life balance by reducing stress and fatigue associated with time-consuming administrative tasks. By alleviating the burden on radiologists, structured reporting contributes to creating a more sustainable and satisfying work environment, ultimately supporting the delivery of high-quality care and enhanced patient outcomes.
The move towards structured reporting has been endorsed by the most reputable radiological societies, such as the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA)6 and the European Society of Radiology (ESR)7. Embracing this evolution is not only essential for addressing current issues but also positions the field to meet the future demands of a rapidly advancing healthcare landscape.
Structured reports: a standardized approach for improving clinical collaboration
Incorporating structured reporting into radiology workflows has the potential to greatly enhance communication in the overall healthcare ecosystem. While traditional, free-text reports offer a comprehensive account of the radiologist’s interpretation of images, they may not always be the most effective means of conveying the findings to referring physicians, especially in the case of complex imaging studies like ultrasound or multi-slice computed tomography (CT), which generate hundreds or thousands of images. By employing a structured reporting approach, communication between radiologists and referring physicians becomes much more streamlined, providing a clear and concise summary of key findings.
Moreover, structured reports can be further enriched by including visual aids such as graphs, charts, schematics, and drawings, which not only help contextualize the findings but also make the information more accessible and easily understood by all members of the healthcare team. These visual elements can significantly enhance interdisciplinary collaboration, allowing healthcare professionals from various specialties to work seamlessly together. This helps create a more comprehensive and informative resource for care providers.
As a result, faster and more informed clinical decisions can be made, reducing the likelihood of miscommunication, errors, and unnecessary follow-up examinations. This ultimately leads to better patient outcomes and more effective healthcare delivery.
Studies have shown8 that radiologists and referring physicians rated structured reports as significantly better than traditional, free-text reports on the following attributes: completeness, clarity, enabling fast extraction of relevant information, facilitating decision-making, and enabling research.
Technological advancements driving the shift
Several drawbacks of structured reporting have been identified, including the time-consuming nature of reporting complex cases using template-based structured reporting, the difficulty of accommodating incidental findings that differ from the suspected diagnosis, and the risk of distraction from the image study when filling in structured reporting templates using a mouse and keyboard9.
It is essential to choose the right IT support to ensure the successful implementation of structured reporting in clinical practice. Radiologists’ time is precious, and a complex setup with multiple disjoint applications for workflow management, image review, and reporting will add friction in making the switch from narrative to structured reporting.
Specially developed tools and services, such as Sectra IDS7 Reporting with its built-in template engine, Sectra Forms, can be the foundation of successful structured reporting implementation.
Sectra IDS7 Reporting is a cohesive “all-in-one” enterprise reporting solution that offers state-of-the-art reporting functionality built into the PACS. Having your worklists, images, and clinical tools, as well as a full-fledged reporting system with best-of-breed speech recognition, all in the same application gives you all the benefits of a PACS-driven workflow without the need for slow and complex multi-application synchronization.
Sectra Forms offers user-friendly interactive forms with native support for structured data collection and storage, speech-enabled workflows, and template sharing capabilities. These features all enhance the efficiency and accuracy of the reporting process.
- Web-based user-customizable forms: streamline data collection and report generation, reducing manual effort and improving the overall workflow.
- Data collection: incorporate PACS data, AI findings, or data from any other external system directly into your report with minimal effort.
- Structured storage: report data is stored in a machine-readable format in addition to the generated report text, enabling subsequent processing for research, analytics, or downstream system integration.
- Speech-enabled workflows: built-in speech recognition allows radiologists to dictate reports directly into the system, enhancing productivity and reducing transcription errors.
- Template sharing: templates can be easily shared across users and departments, promoting standardization and ensuring consistent data quality.
Conclusion
As the volume and complexity of imaging studies continue to grow, structured reporting is emerging as an essential tool for efficient and effective communication between radiologists and referring physicians. It addresses the challenges faced by radiologists while empowering them to work more efficiently, accurately, and effectively. By leveraging structured data, healthcare providers can gain valuable insights, optimize patient care, and advance disease understanding.
Structured reporting is not just a technological advancement; it is a step towards a more data-driven and patient-centric approach to radiology. As we move towards a future where data is at the heart of healthcare decisions, structured reporting will play an increasingly crucial role in enhancing the quality and value of radiological services.
References
- https://www.auntminnie.com/practice-management/article/15659835/complexity-of-radiology-exams-has-skyrocketed
- https://www.beckershospitalreview.com/hospital-physician-relationships/physician-burnout-and-depression-continue-to-climb-medscape.html
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9167391/
- https://pubs.rsna.org/doi/full/10.1148/rg.220037
- https://www.healthaffairs.org/doi/full/10.1377/hlthaff.27.6.1491
- https://www.rsna.org/practice-tools/data-tools-and-standards/radreport-reporting-templates
- https://insightsimaging.springeropen.com/articles/10.1186/s13244-023-01560-0
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10086081/
- https://insightsimaging.springeropen.com/articles/10.1186/s13244-023-01408-7